Nishimura Advanced Ceramic recommends aluminum titanate, which has excellent thermal shock resistance, as the most suitable material for hearth liners for aluminum deposition. We have supplied our products to the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University, and received feedback on thermal shock resistance and power saving.
In terms of power savings, the power consumption has been reduced compared to the conventional hearth liner previously used, dropping from 200mA to 20mA, which is 1/10 the power consumption.
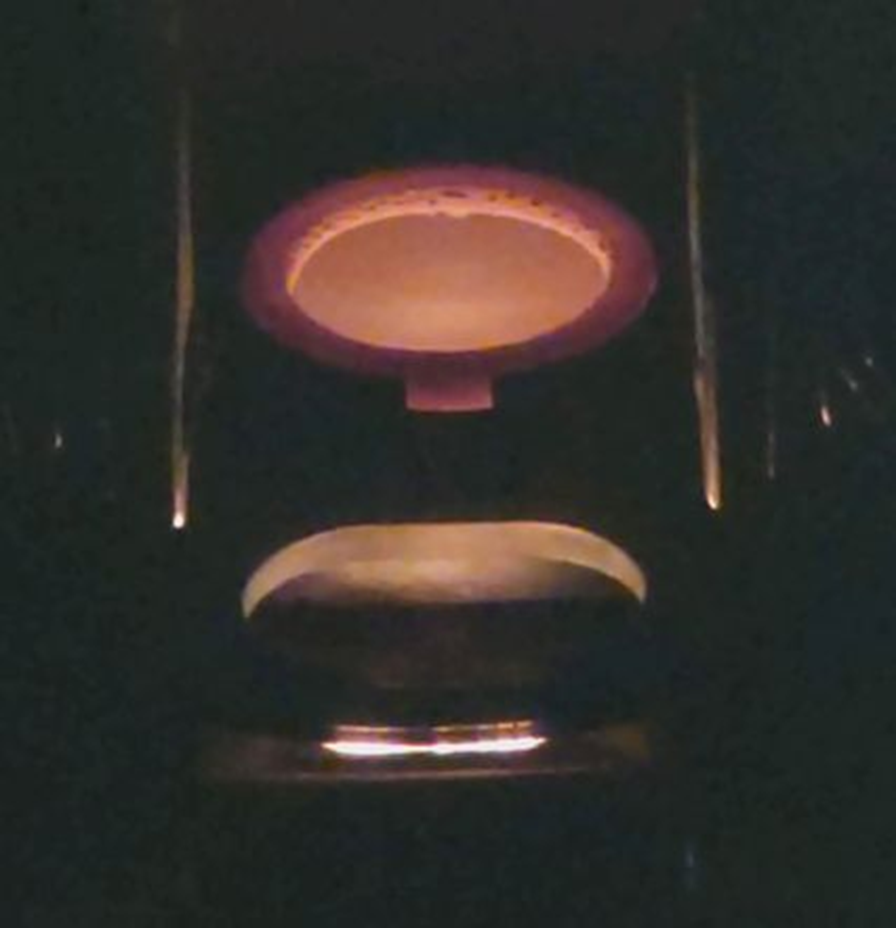

Electron beam irradiation in progress. The image clearly shows that heating is uniform.
Complete resolution of traditional issues!
Issue 1: Ceramic hearth liners tend to crack quickly during the heating phase.
➡️ This product remains intact and can be reused multiple times!
Issue 2: Aluminum vapor deposition material spreads outside the container, leading to time-consuming post-processing cleanup.
➡️ No unwanted spread beyond the container!
Expectations for Energy Efficiency & High-Quality Production
Energy Efficiency
Conventional products allow heat to transfer to the container, causing energy loss and requiring additional power for vapor deposition.
➡️ This product minimizes heat transfer to the container, significantly reducing energy consumption.
Achievements at Osaka University’s Laser Science Institute
| Conventional product | N-420 Aluminum titanate | |
| Power Consumption | 200mA | 20mA |
High-Quality Production
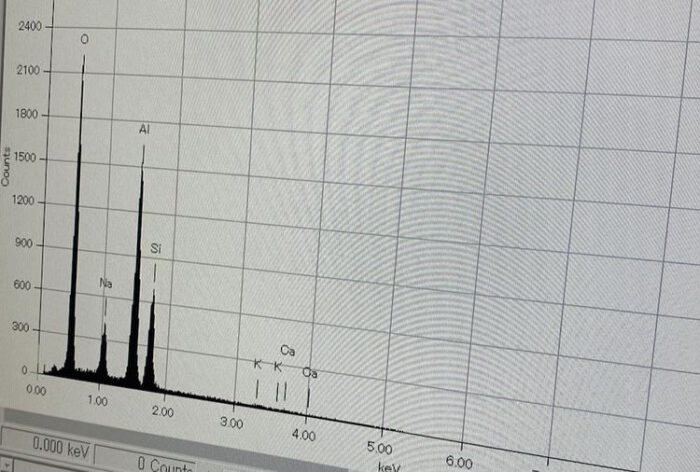
Since there is no energy loss, high-rate vapor deposition is expected, enabling the production of contamination-free products.
In actual deposition tests, no impurity peaks were detected, and only the aluminum material and the base material’s components were identified.
Customizable Shapes
Thanks to our advanced processing technology, the size and shape of the product can be customized freely.
We can accommodate small-batch orders, so feel free to reach out with your requirements!
| Related page: Aluminum Titanate |


![[High-performance power saving] Hearth Liner](https://nishimuraac.com/web/wp-content/uploads/hearthliner02e.jpg)